Wearable Robotics successfully closes its capital increase
Wearable Robotics has successfully closed its capital increase, raising over €2.5 million to support the company’s growth. The Italian firm is an international leader in the field of exoskeletons and wearable robotics.
The round exceeded the initial target of €2 million. ClubDeal Digital syndicated the raise, bringing the total to more than €2.5 million by adding to the capital subscribed through ClubDealOnline’s fully digital platform by Progress Tech Transfer, the investment fund focused on sustainability-driven technologies developed in collaboration with Italian public research; LIFTT, the venture capital holding chaired by entrepreneur-scientist Stefano Buono; and RoboIT, the National Technology Transfer Hub for Robotics and Automation promoted by CDP Venture Capital SGR.
The success of the fundraising was also made possible thanks to the collaboration with Sparkasse Private Banking, following ClubDealOnline’s Private Crowdfunding model.
About Wearable Robotics
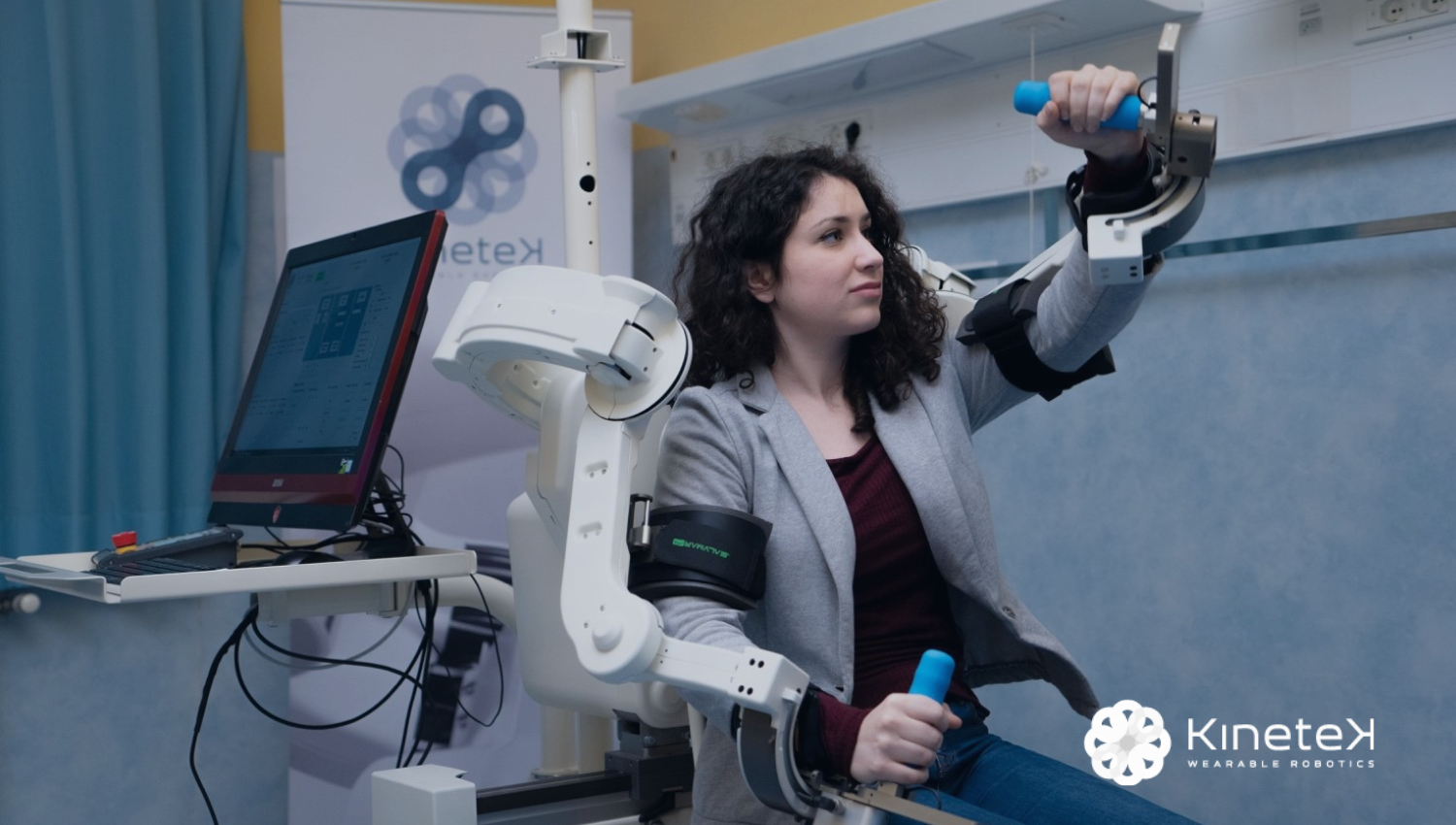
Founded in 2014, Wearable Robotics is an Italian company recognized internationally as a leader in exoskeleton and wearable robotics technologies, specializing in advanced robotic solutions for motor and functional rehabilitation.
The company operates in eight countries and holds seven patents in kinematics, sensors, actuation systems, and exoskeleton design.
Its flagship product is ALEx RS, a wearable robotic device used for upper-limb rehabilitation in stroke patients, operating within a fully virtual environment.
Startup Selection: the role of iStarter
The decision to invest in the company followed a thorough scouting process conducted by iStarter’s Origination team, which, leveraging its exclusive model for Startup and ScaleUp scouting and evaluation, supported ClubDeal Digital throughout the fundraising.
A key contribution also came from Cristiano Fontana, Lead Partner, who has worked in the medical sector for over 15 years.
Wearable Robotics successfully passed a comprehensive assessment, including ESG evaluation.
The investment decision was based on the company’s strong fundamentals and solid market positioning, supporting its ongoing international expansion.
Wearable Robotics already has an active partnership with a major Chinese group for industrial exoskeleton design and is negotiating new agreements with leading sector distributors.